The Electric Charging Business is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing demand for electric vehicles and the growing awareness of sustainable energy solutions. According to Dr. Emily Zhao, a leading expert in the field, “The Electric Charging Business is not just about providing power; it’s about creating a comprehensive ecosystem that supports the transition to cleaner transportation.” This statement encapsulates the essence of the industry, where charging infrastructure plays a pivotal role in facilitating the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs).
As cities worldwide strive to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change, the Electric Charging Business presents significant opportunities for innovation and growth. This sector encompasses a wide range of services, from traditional charging stations to advanced fast-charging networks, all designed to cater to the needs of EV drivers. Understanding how this industry operates is crucial for stakeholders, as it not only informs investment decisions but also shapes the future of transportation.
In essence, the Electric Charging Business is a key player in the shift towards a more sustainable future, bridging the gap between technology and environmental responsibility. With experts like Dr. Zhao leading the charge, the industry is poised to transform how we think about energy consumption and mobility in the coming years.
The electric charging business has been gaining significant traction as the demand for
electric vehicles (EVs) continues to rise globally.
According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), the number of
electric vehicles on the road surpassed 10 million in 2020,
reflecting a 43% increase from the previous year. This surge in EV adoption
has led to a corresponding increase in the need for charging infrastructure, stimulating
investment and growth within the electric charging sector. As of 2021, the global public
charging infrastructure consisted of approximately 1.3 million
charging points, with rapid expansion projected to accommodate future demand.
The landscape of the electric charging business is characterized by diverse charging
solutions, ranging from Level 1 home chargers to
Level 3 rapid charging stations. Industry analyses indicate that the global
electric vehicle charging station market is expected to exceed $30
billion by 2027, driven by technological advancements and regulatory support
aimed at promoting clean transportation. In addition, government incentives and subsidies
play a crucial role in facilitating the transition to electric mobility by encouraging both
consumers and businesses to invest in charging solutions. As urban areas evolve and more
EVs hit the roads, the electric charging business will continue to adapt, innovating to meet
the challenges and opportunities presented by this dynamic market.
Electric charging stations are essential components of the growing electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure. They come in various types, each serving different needs and scenarios. The most common types include Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging stations.
Level 1 charging stations use a standard household outlet, providing a slow charging option, typically delivering about 4 to 5 miles of range per hour. This type is convenient for home charging, as it requires minimal setup and is ideal for overnight charging.
Level 2 chargers, on the other hand, use a 240-volt outlet, significantly reducing charging time, offering around 25 to 30 miles of range per hour. These stations are commonly found in public spaces, parking lots, and workplaces, making them suitable for drivers who require a quicker top-off during their day.
DC fast charging stations are designed for rapid charging, providing an extensive range in a fraction of the time. These stations can deliver up to 80% charge in approximately 30 minutes, making them an excellent option for long-distance travel and highway stopovers. While they are typically more expensive to install and use, their speed and efficiency make them a cornerstone for future EV expansion, helping to alleviate range anxiety and encourage the transition to electric mobility.
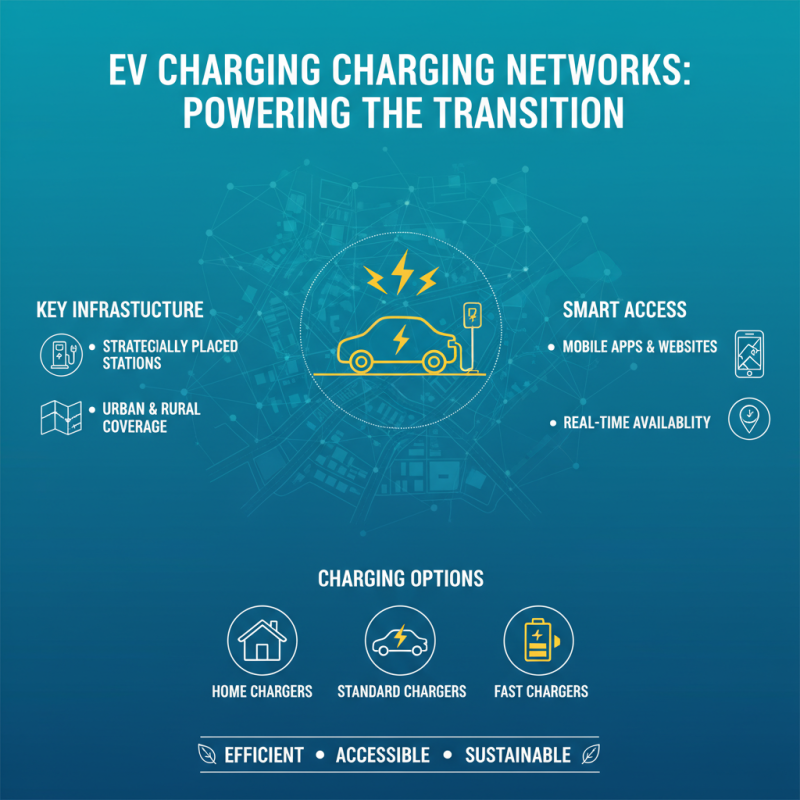
Electric charging networks play a crucial role in the transition to electric vehicles, providing the necessary infrastructure for charging these vehicles efficiently. These networks typically consist of a range of charging stations that are strategically placed across urban and rural landscapes. They are designed to accommodate various electric vehicle models and charging capabilities, from standard home chargers to fast-charging stations. By connecting users through mobile apps and website platforms, these networks facilitate easy access to charging locations, enabling drivers to locate and navigate to the nearest available chargers with real-time availability updates.
The operation of electric charging networks hinges on a complex integration of hardware and software systems. Charging stations are often equipped with user-friendly interfaces that allow for seamless payment options and user account management. Moreover, the networks facilitate smart charging technology, which optimizes charging based on demand, energy prices, and grid capacity. This dynamic management not only benefits users through cost savings and convenience but also promotes the efficient use of renewable energy. Overall, the interconnectedness of charging stations ensures that electric vehicle users have a reliable and accessible means of charging their vehicles, paving the way for a more sustainable transportation future.
In the electric charging industry, various revenue models have emerged as the market evolves and adapts to the increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs). According to a recent report from the International Energy Agency (IEA), the number of electric vehicles on the road is expected to exceed 300 million by 2030, driving significant growth in the charging infrastructure sector. Companies operating in this space often adopt models such as pay-per-use charging, subscription services, and advertising revenue linked to charging station locations.
Pay-per-use charging remains one of the most straightforward models, where EV owners are charged based on the amount of electricity consumed during charging sessions. This model is popular among both public and private charging networks, allowing users to pay only for what they use, with prices often varying by location and charging speed. Alternatively, subscription models offer users a monthly fee for unlimited or discounted access to charging stations, catering to fleet operators and frequent drivers looking to minimize charging costs.
Furthermore, the integration of advertising into charging stations has started to gain traction. As more charging stations are installed in high-traffic areas, providers can monetize these locations by selling advertising space or partnering with local businesses. A report from Bloomberg New Energy Finance highlights that such innovative revenue streams could account for a significant portion of the industry's growth, alongside the traditional electricity sales. Overall, these varied revenue models reflect the dynamic nature of the electric charging business and its critical role in supporting the transition to sustainable transportation.
| Charging Station Type | Average Charging Time | Cost per kWh | Revenue Model | Market Share (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 AC Charger | 8-12 hours | $0.10 - $0.20 | Time of Use Pricing | 30% |
| Level 2 AC Charger | 4-6 hours | $0.15 - $0.30 | Flat Rate | 40% |
| DC Fast Charger | 30-60 minutes | $0.25 - $0.50 | Subscription Model | 25% |
| Wireless Charging | Varies | $0.30 - $0.60 | Pay-Per-Use | 5% |
The future of electric charging technologies is poised for remarkable transformations, driven by advancements in infrastructure, battery efficiency, and renewable energy integration. One significant trend is the development of ultra-fast charging stations that can replenish electric vehicle (EV) batteries in a fraction of the time it currently takes. As battery technology improves, the possibility of charging vehicles to 80% in under 10 minutes is becoming more feasible, making EV usage more convenient for consumers. Additionally, companies are exploring mobile charging solutions, allowing for dynamic and flexible charging options that can be deployed where demand is highest.
Another innovation is the integration of smart charging systems that leverage artificial intelligence to optimize energy distribution. These systems can analyze demand patterns and adjust charging rates accordingly, ensuring that electricity is utilized efficiently and cost-effectively. Furthermore, the rise of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology allows EV owners to sell back excess energy stored in their vehicles, creating a more resilient energy ecosystem and promoting renewable energy usage.
Tips: When considering an electric vehicle, keep an eye on emerging charging technologies, as they may significantly enhance your driving experience. Stay informed about local charging infrastructure developments, as they could impact your charging options and convenience. Additionally, look for EV models that support future charging capabilities to ensure your vehicle remains compatible with upcoming innovations.
This chart illustrates the growth of electric vehicle charging stations in thousands from 2018 to 2023. The increase in charging infrastructure reflects the growing adoption of electric vehicles and the necessity for supporting technologies.






